Inside Aprilia
Photos and Words by Sam Quarelli Fleming
In 1999 Aprilia split its core operations into two locations in Northern Italy. A new assembly plant was opened in Scorze while the design, race, corporate and testing facilities took over the original headquarters a few miles away in Noale. Part I of this pictorial depicts the Scorze assembly plant, part II explores the Noale facility. Neither of these locations have tours for visitors yet so, for the meantime, these pictures will have to suffice.
Part I
Aprilia Production Facility
Scorze, Venezia, Italy

Aprilia is a cutting edge motor company in that it specializes in design, branding, quality and assembly but it subcontracts virtually all of the component manufacturing. You will see many more car companies heading this direction in the future. The assembly plant puts together over one thousand scooter and motorcycles a day. Constructed in 1999, the plant has beautiful modern architecture inside and out.

Here scooter frames arrive from Benelli and are stacked in the parking lot. Most of these will be scooters by the end of the day.

Cast frames for 125cc road bikes. Unfortunately these are not the same type of cast frames as are coming out of Japan right now but it is only a matter of time.

Scooter engines ready for installation. Aprilia buys engines from
multiple sources within Italy as well as Austria and Japan. The plant
produces over 800 scooters and over 200 motorcycles a day.

V60 engines factory fresh from Rotax in Austria destined for RSVs everywhere.

RSV Factory frames from Benelli are patiently waiting their turn on the line.

Where the magic happens. Most of the workers are the Aprilia plant are
contract labor to allow for easier increases or decreases of staffing
levels to match demand for machines.

Aprilia is still a young and relatively small motor company. Like Ducati ten years ago, there are no regular tours of the factory. In our case the person with the best English skills was Paola who is one of the assembly line troubleshooters on the RSV line. When someone has a problem with an assembly operation they illuminate a light and Paola fixes the problem for them. I tried to get her cell phone number so if any of you have any problems with the assembly of your RSVs you would be able to call her directly for the solution but for some reason she would only give the number in Italian.

RSV R (the shiny frames and plain Jane forks give it away) have completed their initial assembly and are staged for the installation of subframes and bodywork.

The entire factory is very stylish and the walls are decorated with pictures
of celebrities on Aprilia products.

Italian style and sensibilities dictate that beauty be everywhere. For that reason the portion of the assembly line dedicated for installation of bodywork is staffed by donne belle giovani.

Aprilia is very stringent about quality control. Each bike is rolling road dyno tested at the end of the assembly line.

Rejected parts are placed in a few bins. The Aprilia plant then has a room with about ten people in it that liaison with the subcontractors and suppliers regarding quality of products provided.

In a room near the end of the assembly line selected vehicles are completely torn down to their component parts to determine if any mistakes or errors where made during the assembly. This feedback loop allows the assembly line to quickly remedy and structural process problems.

The assembly plant is in a separate building a short distance away
from the finished product warehouse. Complete vehicles are loaded
onto a conveyor system which raises them up about forty feet, over
a couple hundred and then back down to ground level in the warehouse.

With 1,200 or so vehicles coming off the line each day this warehouse can fill up quickly. Despite its “Raiders of the Lost Ark” appearance the bikes do not languish here for long.

In keeping with Aprilia’s lean “just in time” delivery system most of these bikes will be shipped out within a week and the whole warehouse is usually turned over within three weeks.
Part II

The Noale complex is spread out amongst a number of different buildings which house the business offices, the race shops for the factory race teams, the corse departments (for the sale of GP bikes), the design shops and the research and development testing centers. Noale also has the original assembly line building which is being converted to an Aprilia museum. Several large signs are decorating the campus from a worldwide Aprilia celebration they hosted in Noale. Valentino Rossi, the most popular racer in Italy, is still featured prominently around Aprilia.
Corse

Aprilia Corse is a separate division within Aprilia. Corse is responsible for the sale of race bikes, sponsorship relations and the management of the factory race teams. Since Aprilia is privately held by Ivano Beggio, basically you have one man writing a check for an entire MotoGP, 250GP and 125GP racing effort. No wonder they eased out of WSBK. Corse has its own offices in this distinct building (there is an interview with Jan Witteveen, the Director of Aprilia Corse, elsewhere in this issue).


Corse is responsible for the supply of spare parts for all Aprilia race bikes in the world. They try to keep parts availability for models produced within the last five years.

The cube is not down to the minimum weight allowed for triples. Carbon wheels and a beautiful carbon swing arm (not shown) indicate how Aprilia plans to get there.

French Italian Didier Lambert works for Corse. Historically attached
to the WSBK program he now works with GP. He is holding an
Aprilia instrument cluster which incorporates the instruments, the
FI management and a data acquisition unit. “It is great unless the
rider crashes a lot”.

This is the factory reference for the building of 125cc GP race bikes. Although a hard number was difficult to pry out of anyone it seemed that Corse produces about 60 125 racers and about 15 250cc racebikes a year which range in specification and, accordingly, price. 250cc racebikes start at $85,000 with a realistic annual budget of about $200,000. Unfortunately this will only get you into the top thirty or so in World GP. Top ten is about $500,000 and top three is $1,000,000. And that is just for the bikes and spares.

Technicians building something fast for Colin.

A Corse technician is putting an Ohlins race shock through some tests on a shock dyno.
The room is equipped to assemble and test both front and rear suspension units.

Run of the mill Ohlins carbon fiber sleeved forks bolted into
testing triple trees for suspension dyno work.

The GP race transporters are lined up across from the GP garages.

Peering into the GP garages (photos were not allowed of the cube and the cube motor)
the transportation crates and victory bottles of champagne are visible. The GP garages
get their very own building which is separate and distinct from the Corse business, parts
and assembly building.
Research and Development

The Halls of Science! Sound proofed rooms off to either side of this
corridor are used to test engines, chassis components and even entire
bikes. This facility is shared by Aprilia Corse, the scooter teams and
the streetbike teams.

Beggio has purchased Moto Guzzi and Laverda. Moto Guzzi is being revived slowly although
its engine blocks still feature the casting to mount the ignition distributor used in the early
1970s. Moto Guzzi products are benefiting from access to the sophisticated Aprilia testing
facilities.

Mike Ambler (Australian) worked for Orbital. Orbital pioneered some of the gasoline based direct injection systems. Direct injection systems introduce fuel straight into the combustion chamber. Various forms of direct injection are used in diesel engines in the US. Aprilia is using direct injection on some of its small scooter engines because direct injection allows for running extremely lean mixtures. Whereas many gasoline motors run best around 14:1 AFR (Air Fuel Ratio) direct injection motors can run at 75 or even 100:1. This allows for low emission scooters which can achieve over 150 miles per gallon. Zoinks. Here Mike watches a Moto Guzzi shock be compressed over and over and over again.
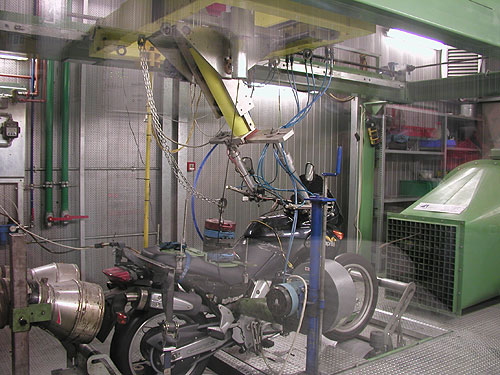
Aprilia is very serious about testing and quality. This rig allows for a virtual rider to activate
the brakes, the clutch, shift gears, open the throttle and weight the seat 24 hours a day for
365 days a year with no chance of accident. The bike can be rigged with a variety of testing
equipment to capture data on wear and tear, temperatures, vibration, noise or any other
indicators. This allows Aprilia to put many miles on its vehicles in a very short period of time
in order to rapidly respond to change in the market while keeping the quality of the final
products very high.

The chassis squeezer. This machine compresses a chassis lengthwise, ie, not up and down
but front to back. The stroke on the machine was about 25mm or so. The scooter chassis,
therefore, has to be able to withstand that amount of flex for a long long time. Built for
Roman paved cobble stone streets of Italy, these scooters should last forever in the US.
An interesting note, any Aprilia aftermarket equipment (tail trunk, mufflers, etc) has
withstood the full range of Aprilia testing for suitability and durability.

Despite the sophisticated testing facility just to the right of this group of young men, sometimes you just need to fire up a 125cc race bike in the parking lot and make some NOISE! These Aprilia technicians demonstrate.
